General certificate data
DiaMina stands for transparency towards its customers.
We consider certificates to be very important in order to be able to operate on the market today.
We only issue certificates for genuine stones where the value of the precious stones is in a profitable ratio
to the cost of the certificate.
Color
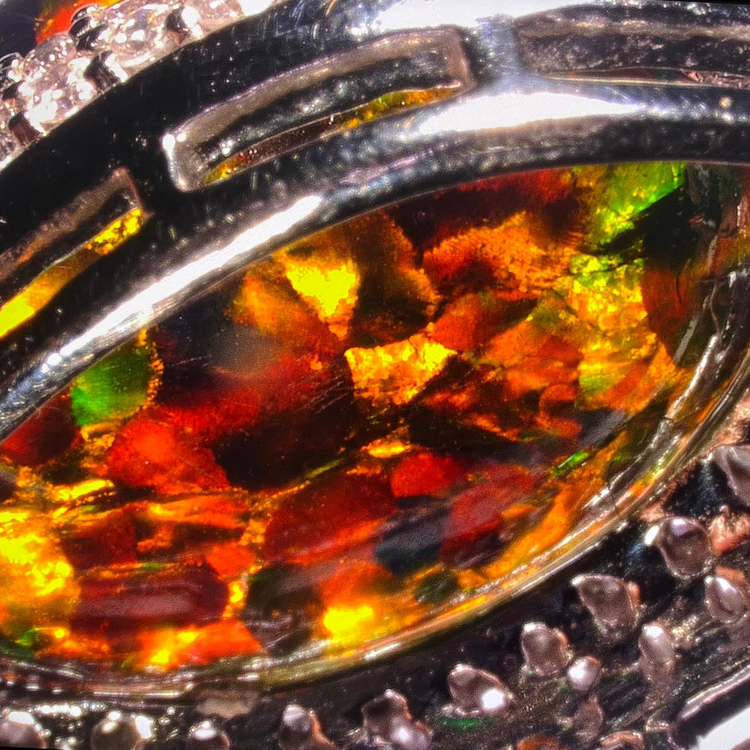

Color
The color of precious stones is one of their most important properties. It results from the chemical composition and the structure of the crystal lattice of the precious stones. Furthermore, it plays a decisive role in quality, partially enabling the determination of origin, and significantly influences the price of the stones.
Not to be underestimated in the precious stones industry is the fashion color of the year, which is what designers in all industries base their new collections on when designing their products, as well as in the world of glitter and the particularly precious.

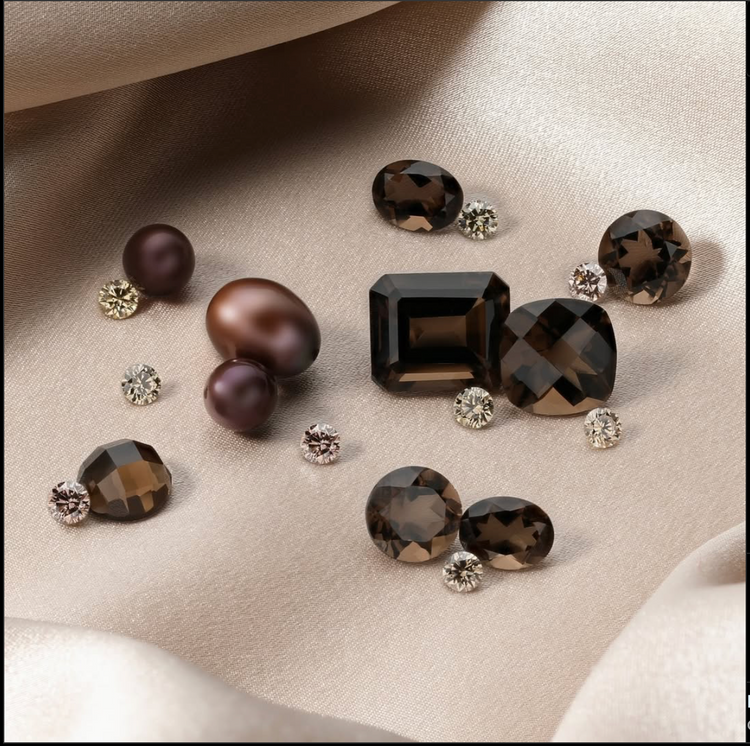
Colorless diamonds
Diamonds are divided into fancy color and colorless diamonds. Over the course of diamond history, the famous and infamous brilliant cut was developed, which greatly enhances the stone's optimal brilliance and light reflection, especially in colorless diamonds.

Fancy diamonds
Fancy colored diamonds, on the other hand, offer a variety of vibrant colors, created by various elements in their chemical structure, and also constitute a distinct market with specific value criteria. The most expensive and rarest are red, pink, green, and blue fancy diamonds with intense color and untreated.

Gemstones
Gemstones are a bit more complex. The most well-known are the "big three," ruby, sapphire, and emerald. However, broadly speaking, most gemstone families exist in all colors, albeit in different varieties, names, and color combinations, often determined by their origin or chemical composition.
Treatments

Treatments
Treatments are a large and very complex topic in the world of precious stones. These are not always easy to prove and can significantly reduce the value of precious stones and reveal a lot about their quality and origin.

Heat treatment
Heating precious stones to improve color and clarity is now a very common technique on the market. There are different methods and heating levels. These methods and heating levels vary depending on the precious stone. However, the heating process is still not always 100% clear and can sometimes be very difficult to determine. This is especially true when heating at low temperatures.
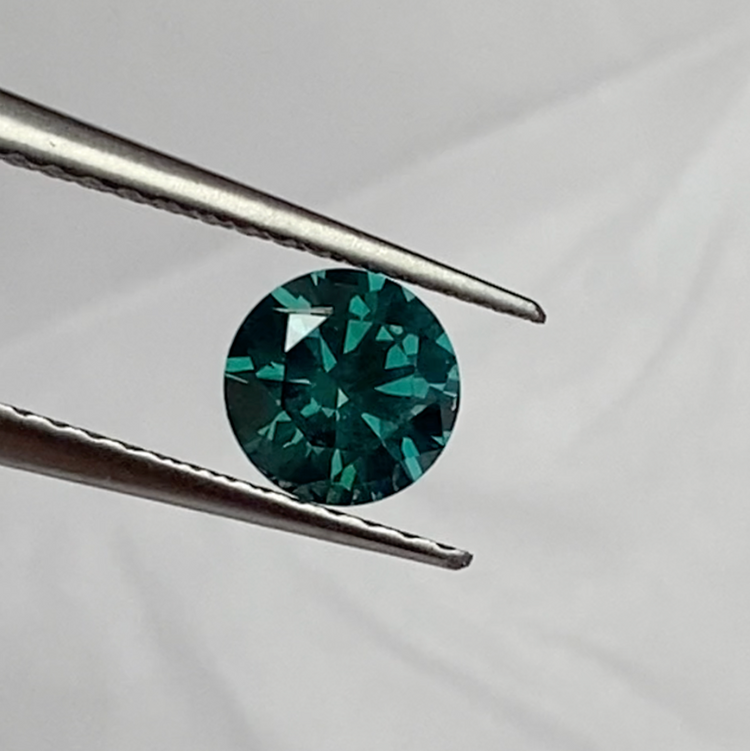

Irradiation
Irradiation of precious stones is a technique increasingly used in the jewelry industry to enhance the color intensity and aesthetic appearance of gemstones. This method is often used on stones such as diamonds, sapphires, emeralds, and others to make them appear more vibrant and colorful. Irradiation can intensify the stone's original color, making the stones more attractive to buyers. However, there is a significant difference in value.
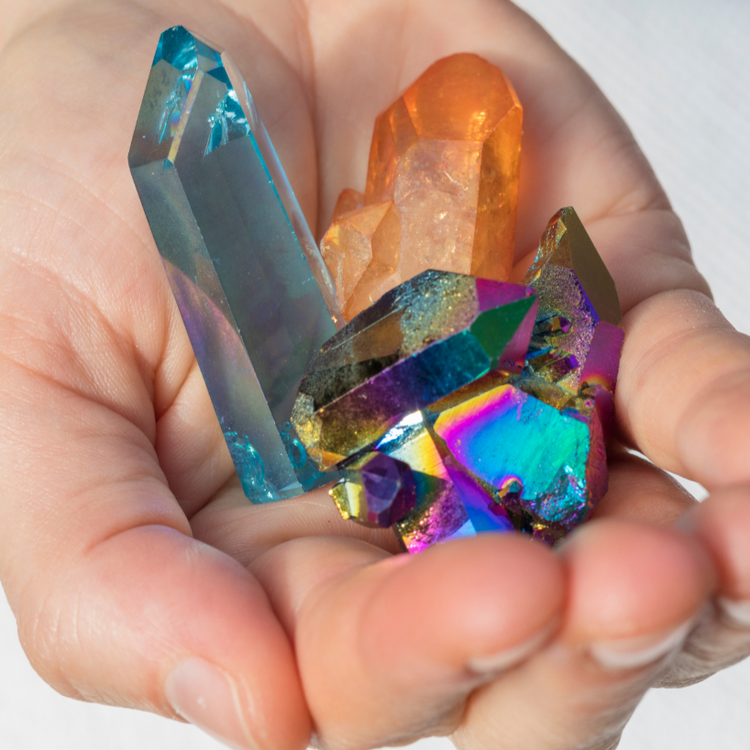

dyeing
This treatment is commonly used on various minerals such as sapphires, tourmalines, topazes, and even diamonds. The goal of coloring is to make the colors more vibrant and uniform, making the stones more appealing to consumers. However, this coloring is not always long-lasting and, in the case of gemstones, also significantly reduces their price.
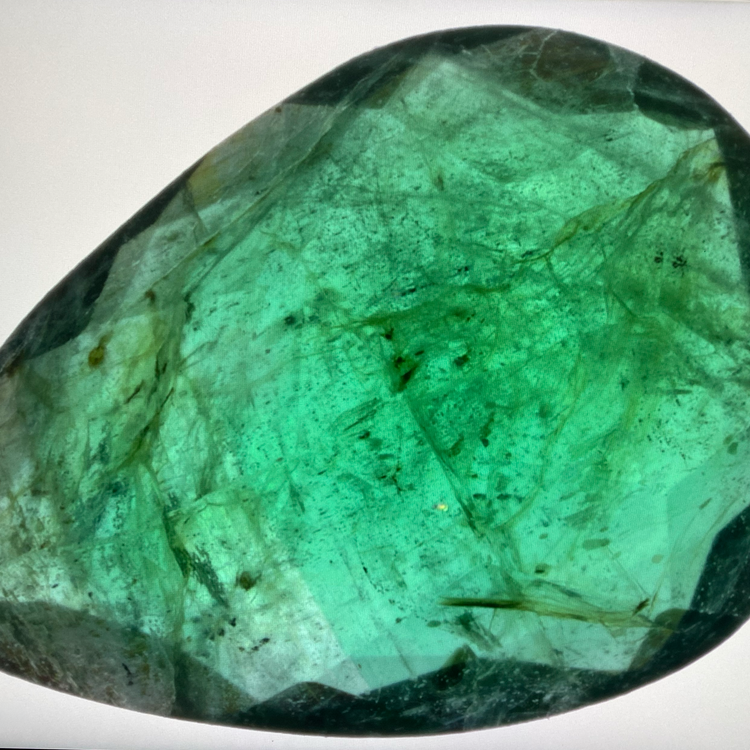

Oil, resin or glass fillings
While emeralds often have natural inclusions and cracks, these treatments help reduce their visibility. Filling the cracks with colorless oil or special resin makes the stone appear clearer and more appealing. However, these treatments also affect the market value of the emerald. Treated stones are generally considered less valuable than untreated specimens, as the fillings are seen as an indication of less naturalness.
Origin
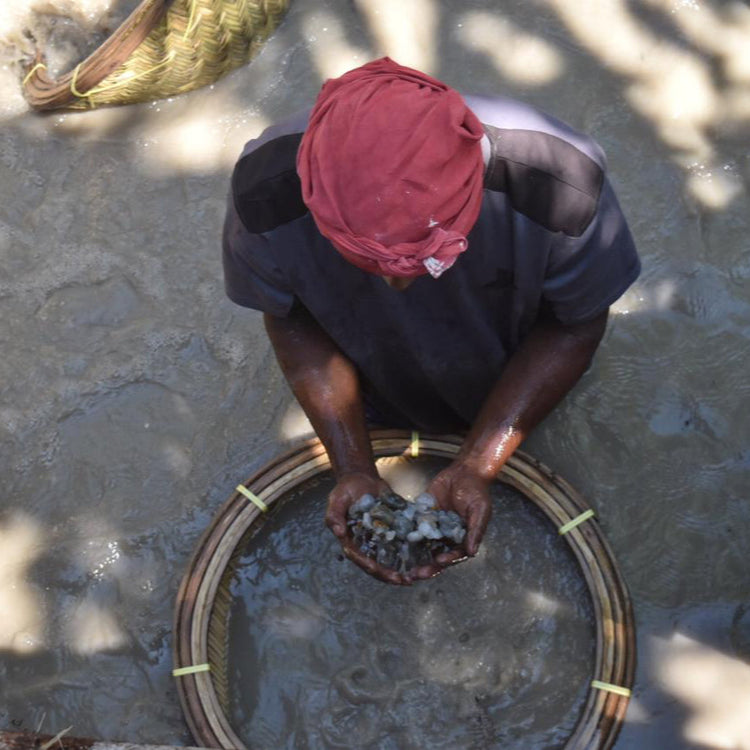

Origin & Development
Precious stones remain a very special time capsule of history. They were formed millions, even billions, of years ago under conditions of enormous heat and pressure. Some of the world's most important gemstone deposits are located in regions such as Brazil, Australia, Russia, India, and Africa. When it comes to certifying precious stones, determining their origin remains the most difficult task.
Authenticity features

Inclusions and history
Inclusions and impurities are very important indicators for determining the authenticity of precious stones. These arise during the formation process and can appear in the form of bubbles, cracks, or other minerals. In contrast to synthetic stones, which are usually too pure and exhibit fewer natural inclusions.
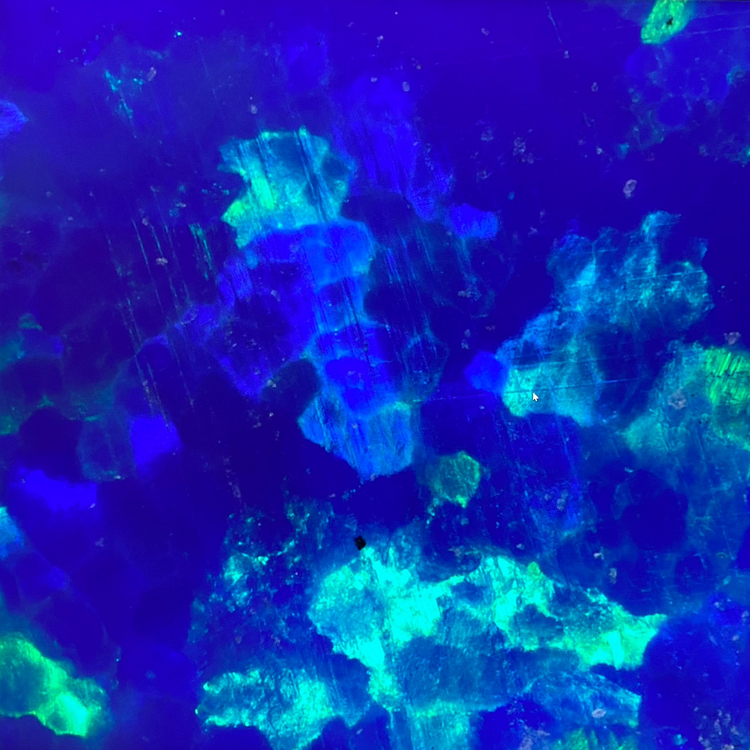

Synthetic precious stones
Too perfect in color, too perfect in clarity, but upon closer inspection, one or two imperfections. Synthetic precious stones are now very common and sometimes very difficult to distinguish.
Photo: Clearly visible growth streaks of a synthetic sapphire
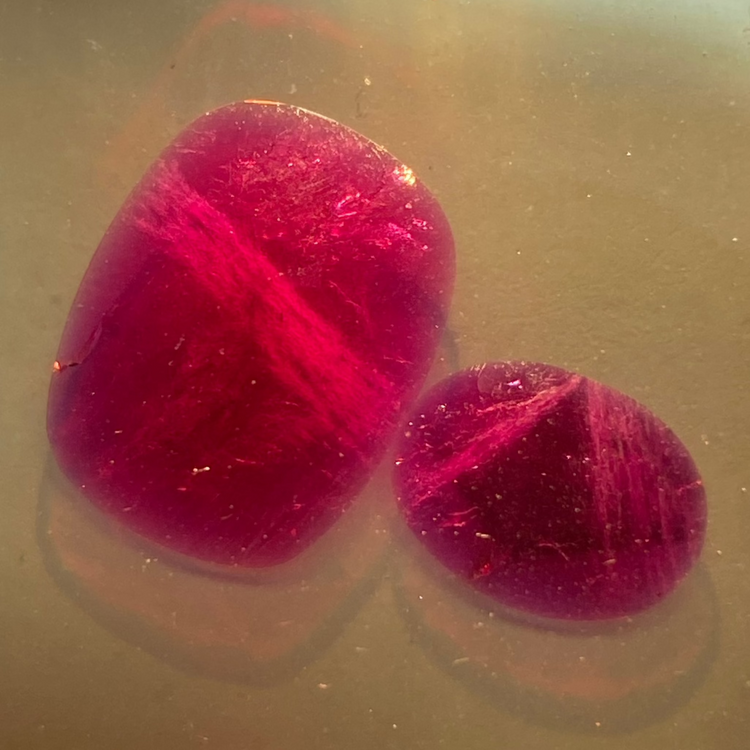

Really synthetic but hardly visible & known
Beware of synthetics that pass as natural. These have almost the same inclusions as genuine stones and boast very high purity and quality.
Photo: Knischka-Rubin
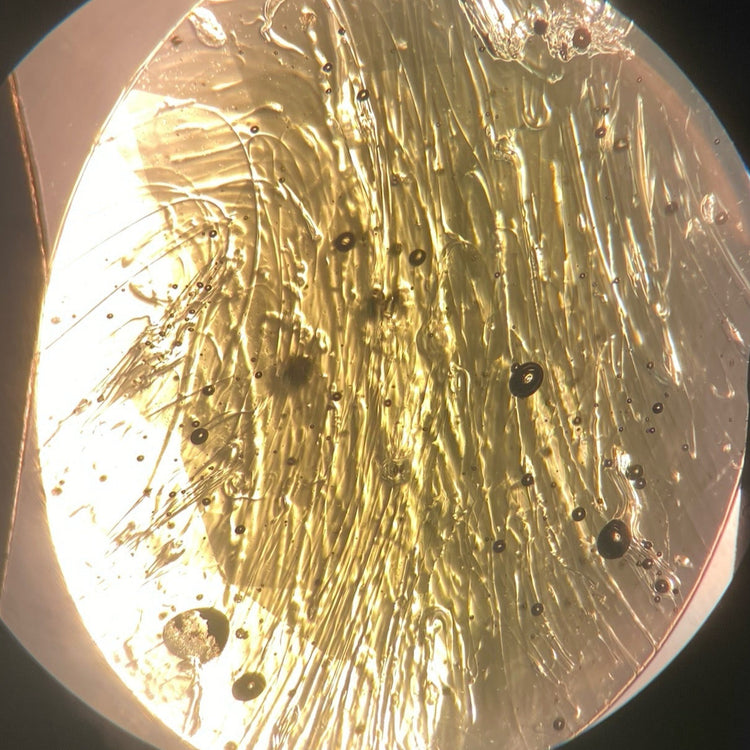
Meteorite glass
Good examples of inclusions are air bubbles and streak-like formations. These indicators, along with the beer-bottle green color, are very telling indicators.
Photo: Inclusion image of a Moldavite
We work according to the CIBJO standards
DiaMina stands for transparency towards its customers. We consider certifications essential for our ability to operate in the market.
We only issue certificates for genuine stones where the value of the precious stones is in reasonable proportion to the cost of the certificate. However, we also issue certificates for non-genuine stones upon request.




